
Recycle your reads!
Overview
Enly is a tool that allows the closure of roughly 10% of the gaps that are commonly present in a draft genome. It is best suited for long reads (e.g. 454 or Sanger reads) and is based on the iterative mapping of reads at the extremities of contigs obtained after de novo assembling.
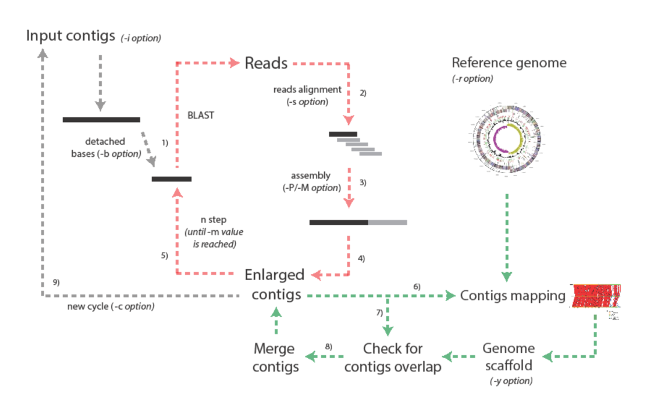
The overall strategy of the tool is schematically reported in Figure 1. Enly takes a multiFASTA file embedding all the contigs and tries to increase their length by reiterating the following procedure for each of the contigs. Initially, a number of bases (selectable by the user) are detached from one of the contig extremity and this sequence fragment is used as input for a BLAST search against a database embedding all the reads resulting from the sequencing run. Since a typical 454 sequencing run embeds reads with variable lengths, different BLAST searches are performed, using fragments of different length at every step within the same cycle. We suggest to explore different fragments lengths (-b and –m parameters, see below) ranging from 100/200 bp greater than the average reads length to 100/200 bp lower than average reads length. The BLAST output is then parsed to identify those reads that can be used to increase the overall length of the contig, that is those reads only partially aligned at the end of the contig and projecting outside from its extremity. The identified reads and the original contig are then assembled together resulting in a (possibly) enlarged contig. The same procedure is repeated for the other extremity of the contig. These steps are repeated for a certain (user specifiable) cycles, or until no further elongation of the contigs is possible.
Requirements
ENLY was developed and thoroughly tested in a Linux environment, but has been succesfully run on Windows (using Cygwin), Mac OSX and has been reported to work on BSD.It has a few software requirements, listed below:
- GCC compiler with C++ support
- Python
- BioPython
- Perl
- Blast and Blast+
- cdbfasta / cdbyank
- At least one assembler between Phrap (freely available on request, ask for 1.09 version) and Minimo
Outputs
The outputs of ENLY consist of the enlarged contigs and various files summarizing what happened during the enlarge steps.Enlarged contigs
You will find a multiFASTA file with the enlarged contigs for each cycle ENLY went through, and the single FASTA files for each contig, both in its original form (selected_contigs_n) and the enlarged one (selected_contigs_n_ext).Statistics
Files called length_En features the length of the contigs at the n-th cycle.OverlapPLUS and OverlapMINUS contains information about the closed gaps at each extremity (5' and 3') of the contigs.

Quick reference
Installation
Run with default parameters
Help
Command line options
Compulsory parameters
- -i Input File Name [your contigs file name]
- -b Bases to detach at first cycle [recommended: a value 100/200 greater than the average reads length]
- -m Minimum bases to detach [recommended: a value 100/200 lower than the average reads length]
Optional parameters
- -c Maximum number of cycles [default is 10]
- -a Assembler ["P" Phrap or "M" Minimo, default is Phrap, CASE SENSITIVE OPTION!]
- -r Reference genome [FASTA file name]
- -s Alignment % threshold during reads mapping [default is 80]
- -d Bases to detach at every step [default is 50 bp]
- -p Number of cores [default is 4, requires MPI]
- -y Scaffold file used for validation of contigs merging

Changelog
Version 1.2.2:
- Merged contigs are listed in a specific file (one for each cycle) named MergedContigs_cycle*
- Some changes concerning the font color during the output printing on screen
Version 1.2.1:
- Small bugfix to make possible the use of Enly without a reference genome or a scaffold order
Version 1.2:
- Improved efficiency, more gaps are closed
- If your contigs are scaffolded, you can use this information to improve the gap closing
- Various bugfixes and code cleanup
Version 1.0:
- First version
